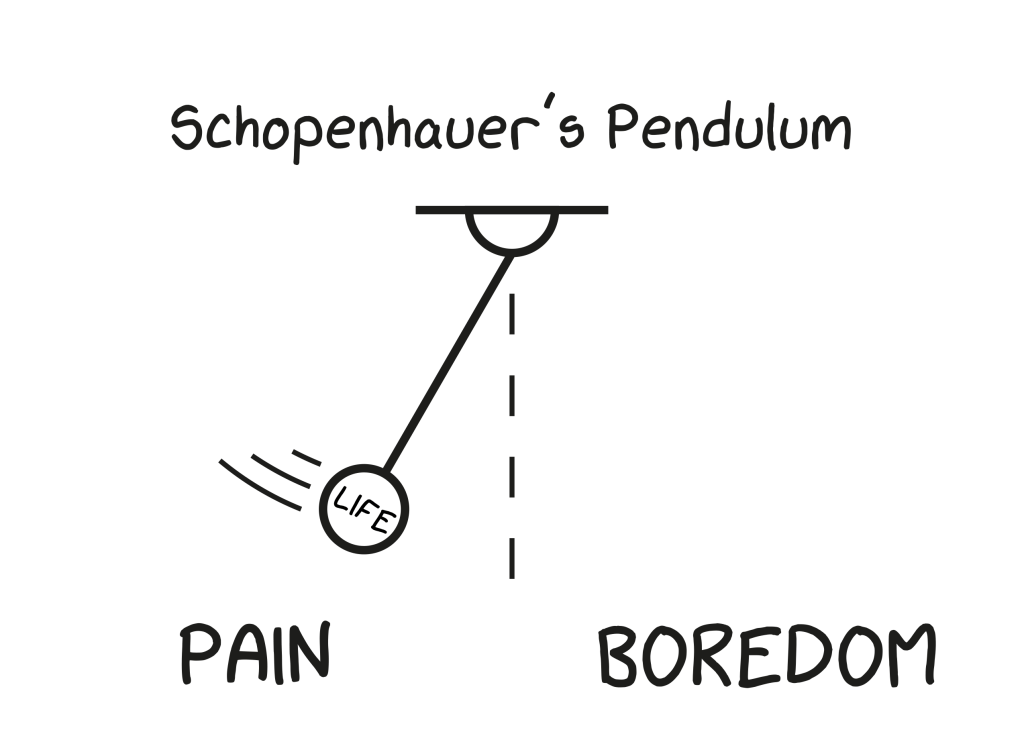
Why Aren’t Smart People Happier?
A good name for problems on tests that determine someone’s level of intelligence is “well-defined.” Well-defined problems can be very difficult, but they aren’t mystical. You can write down instructions for solving them. And you can put them on a test. In fact, standardized tests items must be well-defined problems, because they require indisputable answers. Matching a word to its synonym, finding the area of a trapezoid, putting pictures in the correct order—all common tasks on IQ tests—are well-defined problems.
People differ in their ability to solve well-defined problems, they’re not the only kind of problems. “Why can’t I find someone to spend my life with?” “Should I be a dentist or a dancer?” and “How do I get my child to stop crying?” are all important but “poorly defined” problems. Getting better at rotating shapes or remembering state capitals is not going to help you solve them.
One way to spot people who are good at solving poorly defined problems is to look for people who feel good about their lives; “how do I live a life I like” is a humdinger of a poorly defined problem. The rules aren’t stable: what makes you happy may make me miserable. The boundaries aren’t clear: literally anything I do could make me more happy or less happy. The problems are not repeatable: what made me happy when I was 21 may not make me happy when I’m 31.
This is why the people who score well on intelligence tests and win lots of chess games are no happier than the people who flunk the tests and lose at chess: well-defined and poorly defined problems require completely different problem-solving skills. Nobody agrees on the rules, the pieces do whatever they want, and the board covers the whole globe, as well as the inside of your head and possibly several metaphysical planes as well.
Over the last generation, we have solved tons of well-defined problems. We eradicated smallpox and polio. We landed on the moon. We built better cars, refrigerators, and televisions. We even got ~15 IQ points smarter. How much did our happiness improve? None.

We haven’t yet defined the problem of “living a happy life”. We know that if you’re starving, lonely, or in pain, you’ll probably get happier if you get food, friends, and relief. After that, the returns diminish very quickly. You could read all the positive psychology you want, take the online version of The Science of Wellbeing, read posts on hacking the hedonic treadmill, meditate, exercise, and keep a gratitude journal—and after all that, maybe you’ll be a smidge happier. Whatever else you think will put a big, permanent smile on your face, you’re probably wrong.
We fawn over people who are good at solving well-defined problems. They get to be called “professor” and “doctor.” We pay them lots of money to teach us stuff. They get to join exclusive clubs like Mensa and the Prometheus Society.
People who are good at solving poorly defined problems don’t get the same kind of kudos. They don’t get any special titles or clubs. There is no test they can take that will spit out a big, honking number that will make everybody respect them.
And that’s a shame. My grandma does not know how to use the “input” button on her TV’s remote control, but she does know how to raise a family full of good people who love each other, how to carry on through a tragedy, and how to make the perfect pumpkin pie.
If you don’t value the ability to solve poorly defined problems, you’ll never get more of it. You won’t seek out people who have that ability and try to learn from them, nor will you listen to them when they have something important to say. You’ll spend your whole life trying to solve problems with cleverness when what you really need is wisdom. And you’ll wonder why it never really seems to work. All of your optimizing, your straining to achieve and advance, your ruthless crusade to eliminate all of the well-defined problems from your life—it doesn’t actually seem make your life any better.

_________________________
‘I realized I’d been ChatGPT-ed into bed’: how ‘Chatfishing’ made finding love on dating apps even weirder.
Standing outside the pub, 36-year-old business owner Rachel took a final tug on her vape and steeled herself to meet the man she’d spent the last three weeks opening up to. They’d matched on the dating app Hinge and built a rapport that quickly became something deeper. “From the beginning he was asking very open-ended questions, and that felt refreshing,” says Rachel.
One early message from her match read: “I’ve been reading a bit about attachment styles lately, it’s helped me to understand myself better – and the type of partner I should be looking for. Have you ever looked at yours? Do you know your attachment style?” “It was like he was genuinely trying to get to know me on a deeper level. The questions felt a lot more thoughtful than the usual, ‘How’s your day going?’” she says.
Soon, Rachel and her match were speaking daily, their conversations running the gamut from the ridiculous (favourite memes, ketchup v mayonnaise) to the sublime (expectations in love, childhood traumas). Often they’d have late-night exchanges that left her staring at her phone long after she should have been asleep. “They were like things that you read in self-help books – really personal conversations about who we are and what we want for our lives,” she says.
Which is why the man who greeted her inside the pub – polite, pleasant but oddly flat – felt like a stranger. Gone was the quickfire wit and playful rhythm she’d come to expect from their exchanges. Over pints he stumbled through small talk, checked his phone a little too often, and seemed to wilt under the pressure of her questions. “I felt like I was sitting opposite someone I’d never even spoken to,” she says. “I tried to have the same sort of conversation as we’d been having online, but it was like, ‘Knock, knock, is anyone home?’ – like he knew basically nothing about me. That’s when I suspected he’d been using AI.”
Rachel gave her date the benefit of the doubt. “I thought maybe he was nervous,” she says. But she’d been “Chatfished” before, so when the gap between his real and digital selves failed to close on their second date, she called it off. “I’d already been ChatGPT-ed into bed at least once. I didn’t want it to happen again.”
In a landscape where text-based communication plays an outsized role in the search for love, it’s perhaps understandable that some of us reach for AI’s helping hand – not everyone gives good text. Some Chatfishers, though, go to greater extremes, outsourcing entire conversations to ChatGPT, leaving their match in a dystopian hall of mirrors: believing they’re building a genuine connection with another human being when in reality they’re opening up to an algorithm trained to reflect their desires back to them.

_______________________________
Youtube is eating everything: