My father didn’t meditate, didn’t track his steps or explicitly “exercise,” and never once uttered the word “mindfulness.” Yet he lived to 92, dying at home after a very short bout with brain cancer, having been visited by his children and 11 grandchildren in the 10 days between diagnosis and death. And my mom is still going strong at 92. She still has her sense of humor and her political engagement but no “diseases that will kill her,” as she puts it.
I have spent my professional life studying what makes people live healthier and longer. I have analyzed data sets on longevity the world over and reviewed hundreds of clinical studies. I have heard numerous new claims about supplements, diets and tech devices that are supposed to extend life. But nothing I have read in the scientific literature explains longevity better than the lives of my incorrigibly social parents, Benjamin and Marsha Emanuel.
My father was a pediatrician who spoke five languages and was comfortable talking to anyone and everyone. He routinely talked to strangers, offering suggestions based on his well-honed diagnostic skills.
Whenever we stopped in a restaurant he would start chatting with the people at the next table within five minutes—asking about their jobs, their families, where they were from and what they liked about the place they lived. If no one was at a nearby table, he would strike up a conversation with the waitress.
To a modern eye, this might seem overzealous. But people responded to him. They felt seen, not interrogated. There was no agenda—just my father’s insatiable curiosity about people. One time, a casual chat with another father in a park ended with an invitation for our whole family to dinner at their home.
My mom was also incurably social. Our house was constantly filled with the people she collected. She was great at making our teenage friends feel understood, with warmth and empathy. When her kids went off to college, she finished her training as a therapist and went into practice.
For years, I did not fully appreciate what I was witnessing. To me as a kid, my father’s endless chatter was an embarrassing quirk of his personality. And my mother’s welcoming of strangers into our home just seemed, well, normal. Only after decades as a physician and policymaker did I understand that my father and mother had unintentionally but eagerly adopted one of the most powerful health interventions ever discovered: human connection.
Study after study now confirms what my father and mother intuited long before science caught up. Social relationships, both the deep ones and the fleeting exchanges, reduce stress hormones, lower blood pressure, reduce inflammation, strengthen immune function and make you happier. They may even slow cellular aging.
An analysis by the Health and Retirement Study, which enrolled over 20,000 Americans older than 50, found that over the next eight years, people with the most close friends (an average of 7.8) had a 17% lower risk of depression and a 24% lower risk of dying compared with people who had fewer close friends (an average of 1.6).
Similarly, Harvard University’s Study of Adult Development, which followed people for over 80 years, found that “the people who were happiest, stayed healthiest as they grew old, and who lived the longest were the people who had the warmest connections with other people.” By contrast, social isolation is as dangerous to longevity and cognitive decline as being obese. My father didn’t need PubMed to know that being interested in people kept him not just alive but vibrant and energetic.
Years later, I came to see that impulse—to notice, to care, to connect and help—as the very definition of wellness. My father’s memorial service overflowed with friends, former patients and neighbors, each one with a story about how he’d helped them, laughed with them or simply made them feel less alone. Every Thursday, meanwhile, my mom still has lunch at the deli with “the boys”—friends she has collected over the years.
It has taken me many years to grasp that wellness is inherent in the community we inhabit. My father’s conversations with strangers weren’t just good for him but for the people he engaged with. My mother’s weekly lunch is both good for her and for all her friends. Sharing time with others is beneficial for all involved.
If there is a “longevity hack,” that is it. Forget the cold plunges, red lights and fad-driven supplements. Call a friend. Chat with your neighbor. Ask the Uber driver or grocery checkout clerk how their day is going or how their holidays were. When I think of my father and mother now, I realize that health isn’t something you achieve in isolation. It is something we all create together.

_____________________________
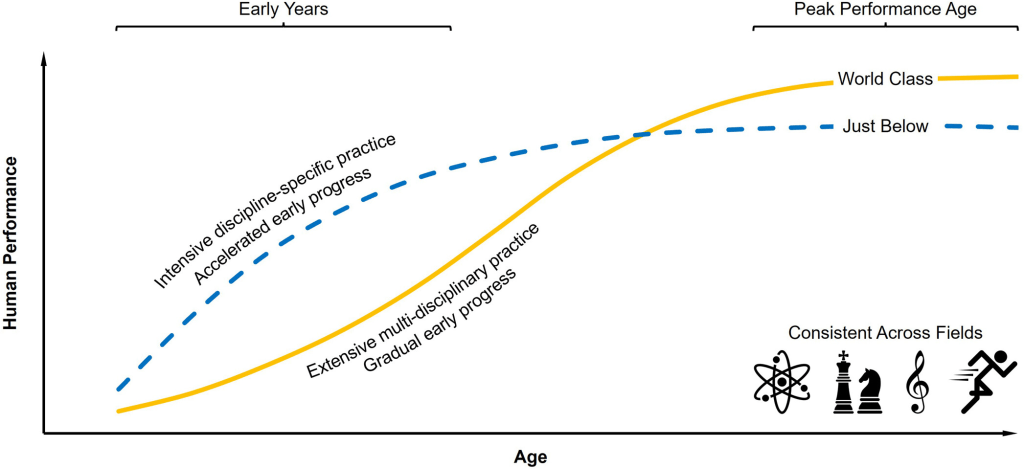
From athletes like Simone Biles and Michael Phelps to scientists like Marie Curie and Albert Einstein, identifying exceptional talent is essential in the science of innovation. But how does talent originate? Did the most talented athletes, scientists, and musicians reach peak performance relatively early or late in their career? Did they forgo mastering multiple sports, academic subjects, and musical instruments to reach world-class performance in only one?
An analytical review looked at published research in science, music, chess, and sports and found two patterns: Exceptional young performers reached their peak quickly but narrowly mastered only one interest (e.g., one sport). By contrast, exceptional adults reached peak performance gradually with broader, multidisciplinary practice.
______________________________
Nearly two decades of studies from multiple independent labs suggest that a father’s gametes shuttle more than DNA: Within a sperm’s minuscule head are stowaway molecules, which enter the egg and convey information about the father’s fitness, such as diet, exercise habits and stress levels, to his offspring. These non-DNA transfers may influence genomic activity that boots up during and after fertilization, exerting some control over the embryo’s development and influencing the adult they will become.
The findings could end up changing the way we think about heredity. They suggest that what we do in this life affects the next generation. What a father eats, drinks, inhales, is stressed by or otherwise experiences in the weeks and months before he conceives a child might be encoded in molecules, packaged into his sperm cells and transmitted to his future kid.

___________________________
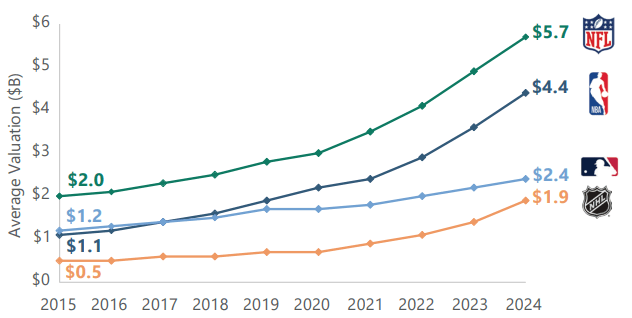
The average team valuation by league (in billions):
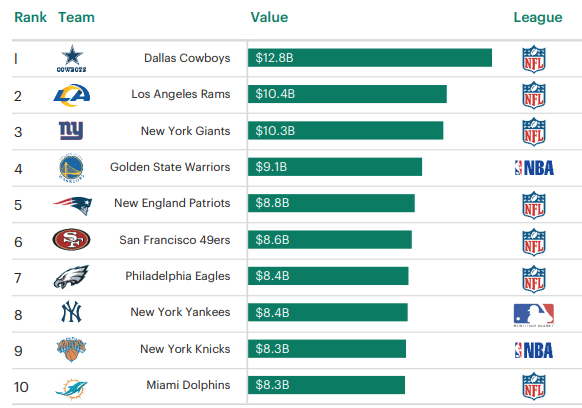
The top 10 most valuable pro sports teams in the U.S.:
North American sports assets (RASFI) returns vs. other asset classes, and why private credit wants to get more involved in the industry.