There’s a new theory from an amateur code-breaker, Alex Barber, that links two of America’s most infamous unsolved cases: the 1947 mutilation murder of Elizabeth Short (known as the Black Dahlia) and the late-1960s killings by the Zodiac Killer.
Baber, a 50-year-old self-taught investigator from West Virginia with autism and no formal education beyond high school, claims both crimes were committed by the same person: Marvin Margolis (who later used the alias Marvin Merrill until his death in 1993). Baber says he cracked the Zodiac’s unsolved 13-symbol cipher (Z13) using AI-assisted methods, revealing the name “Marvin Merrill.” He connects this to the Black Dahlia case through circumstantial links, including:
- Margolis’s brief living arrangement with Short shortly before her murder.
- His Navy medical training explaining the surgical precision in her dismemberment.
- A 1992 sketch by Margolis titled “Elizabeth” depicting a mutilated woman with the word “ZODIAC” hidden in the shading.
- The possible murder site near a Compton motel called the Zodiac Motel, which Baber suggests inspired the killer’s later moniker.

_________________________
The 2018 US semiconductor embargo against China changed the world. The age of cooperation and globalization was over.
With the 2018 embargo, the US essentially punched China on the nose. At the time, China had little choice but to take the punch. Take the punch and prepare its own economy for a future in which it would be less vulnerable to further US embargoes.
For seven long years China went on a diet, and went to the CrossFit gym. And as all of China’s savings were captured—through tighter capital controls, the suspension of IPOs, and the concentration of bank lending—and redirected towards China’s industrial supply chains, returns for investors were dreadful.
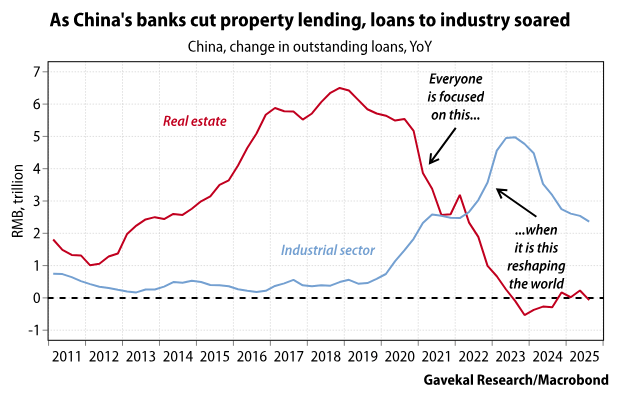
When Donald Trump came back to power in 2025, China, which had spent the past seven years getting toned, showed up and essentially said: “Gloves off. If you want a fight, let’s go. You tariff me, then I will tariff you. You embargo me, then I will embargo you.
China’s response was to de-Westernize its supply chain, at great cost to its investor base, to economic growth, to domestic consumption and even to its birth rate.
Meanwhile, over the same period, the US did absolutely nothing to de-Sinify its own supply chain. While China hit the gym, the US partied. And partied hard: US budget deficits expanded, but pretty much just funded expansions in social benefits—social security, Medicare and Medicaid. Between 2018 and 2025, US government debt increased from $21 trillion to $38 trillion. However, none of the US $17 trillion in debt went into building new Hoover dams, new Tennessee Valley Authorities, new interstate highways or new railroads.
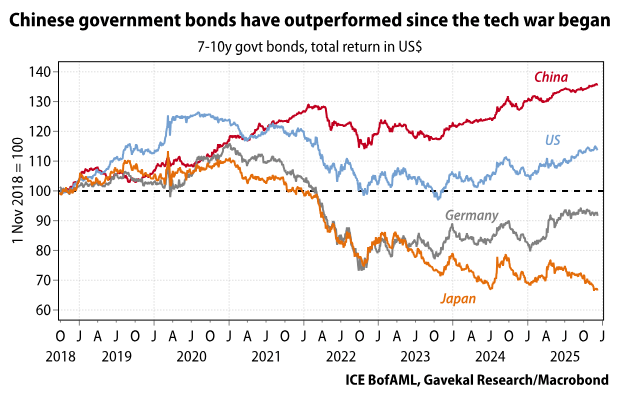
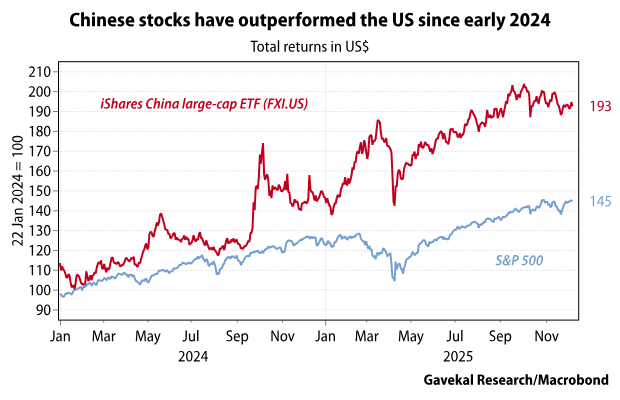
China’s push to de-Westernize its supply chains came at great cost to the Chinese economy and Chinese society. Would US policymakers countenance such judicial repression?

______________________________________
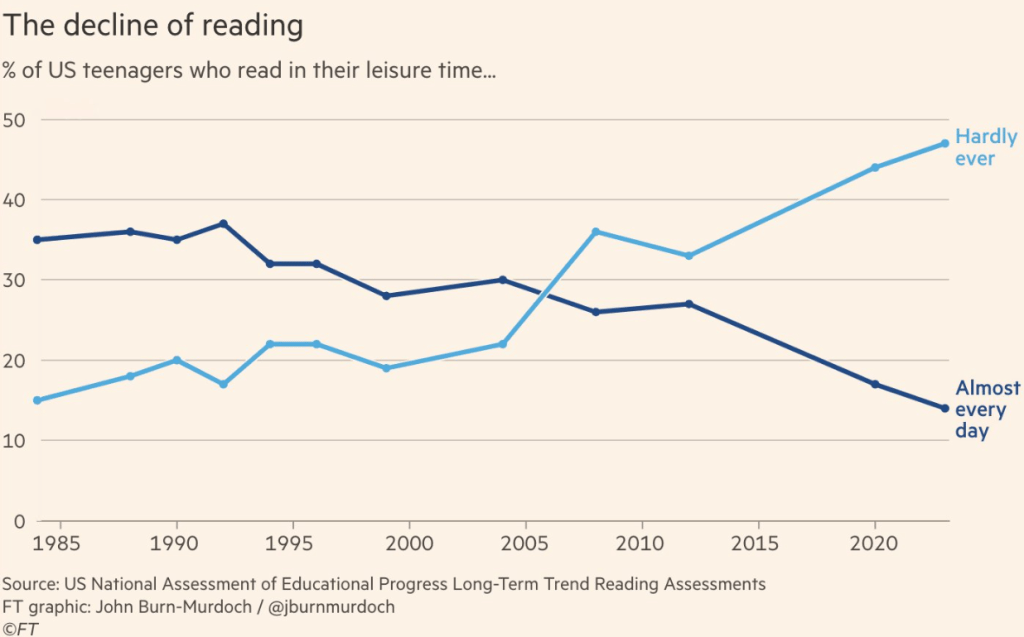
Readers used to outnumber non-readers 2 to 1. Now non-readers outnumber readers 3 to 1.
____________________________
________________________________
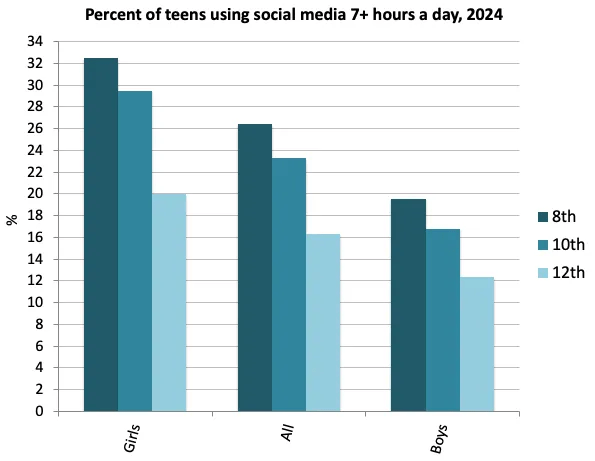
The frustrating truth is that we don’t really know for sure what the digital empire of short-form video is doing to our minds. But a systematic review of 71 studies with 98,000 participants published in 2025 reached an alarming finding. Across the dozens of studies, heavy short-form video users showed moderate deficits in attention, inhibitory control, and memory.
Several studies in the meta-analysis reported structural and functional differences in the prefrontal cortex and reward circuits among high-frequency users, while others found cognitive flexibility reductions and altered dopaminergic reward responses. None of this proves causation. But taken together, they suggest a plausible mechanism: a daily diet of hyper-rewarding, rapid-fire stimuli may gradually reshape attention and regulatory systems in ways that weaken our attentional control.
________________________________
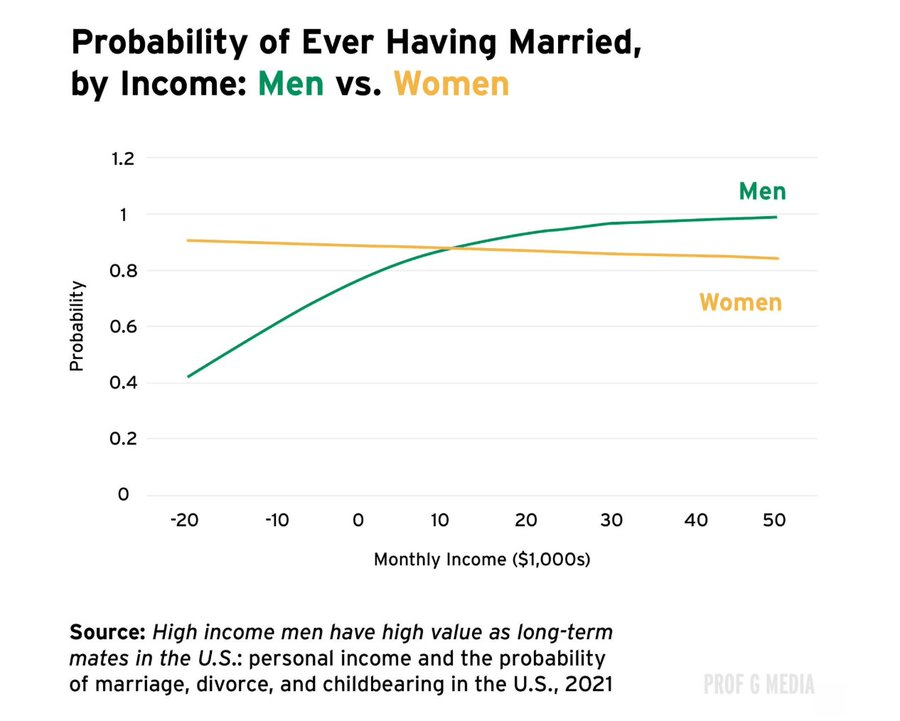
The probability of men getting married increases with their income.
________________________________
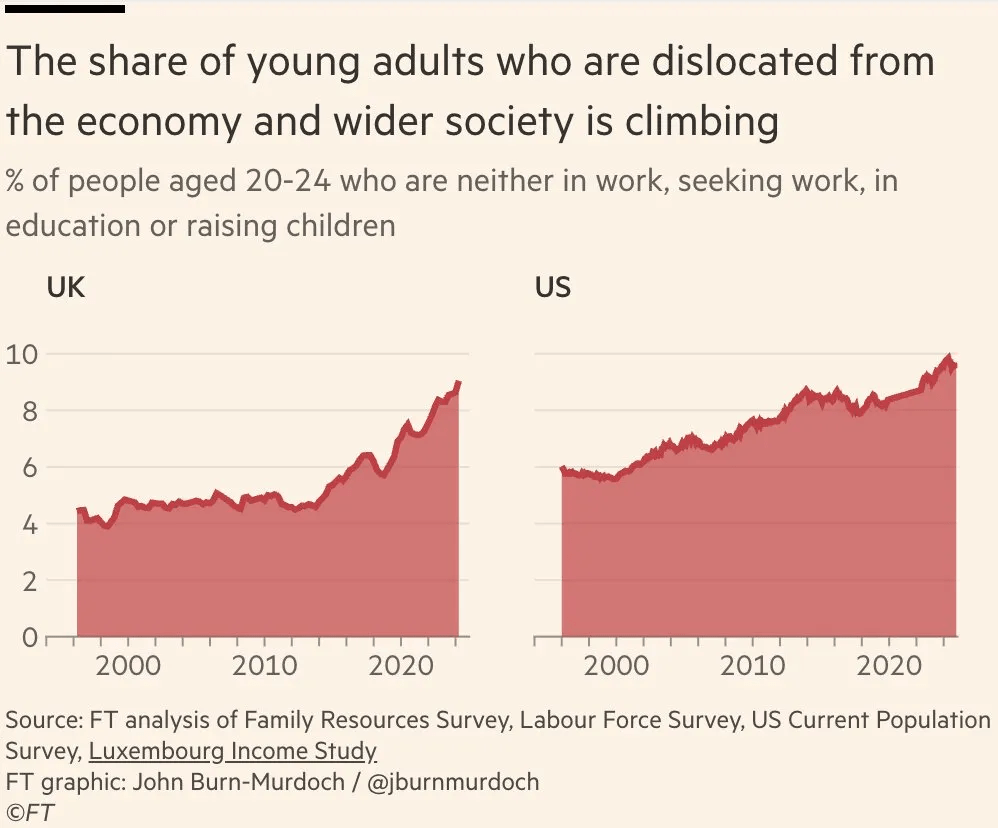
The share of people between 20 and 24 who are not in a job, or seeking work, or in school, or raising a child has nearly doubled in the last quarter-century in both the UK and the U.S.
________________________________
- Walk 15+ miles a week, even if you do other exercise.
- Eat real food. Not too much.
- Stop drinking alcohol, even in moderation.
- Explore minimalism (it’s not what you think it is).
- Get 8 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Invest in experiences, not things.
- Stay lean. Men in particular are obsessed with muscle mass these days, but bulk doesn’t age well. The goal is to be strong but lean. The fittest guys in their 50s and beyond aren’t meatheads, they’re lean guys who are serious about a sport.
- Stop drinking sodas and sugary energy drinks.
- Show up on time, every time. Poor time management limits success more than most people realize.
- Find a hobby and pursue mastery. You can’t have a happy life without a passionate pursuit that isn’t your vocation. Your work—even if you enjoy it—isn’t enough.
- Try psychedelics. It’s one of those things everyone should do at least once, and it might be the breakthrough you’ve been looking for.
- Be a lifelong learner. Your brain is just like a muscle—if you don’t feed and flex it regularly, it will atrophy.
- Find your purpose. People with a strong sense of purpose are happier and live longer. Lack of purpose sucks energy and magnifies depression.
- Only take advice from people who embody the traits you want to have. Talk is cheap—emulate those who have done it.
- The goal is not to retire and do nothing, it’s to build a great day-to-day life that you don’t need to escape. A life of leisure is a slow death.
- Have fun! Do frivolous and silly things that make you smile.
- Accumulate assets—things that grow in value over time. It’s the #1 habit of rich people, and it can be done in tiny chunks. It becomes addictive (in a good way).
- Make your own decisions. We live in an era where most of what society tells us is wrong. Don’t be afraid to break from societal norms.
- Go all in on family. Get married, stay married, have kids. Burn the boats. In the end, family is all that matters.
- Be ruthless with your time. Money comes and goes. Time only goes. Audit your calendar ruthlessly—cut the trivial, double down on the meaningful, and spend your hours like your life depends on it.
_____________________________
________________________________
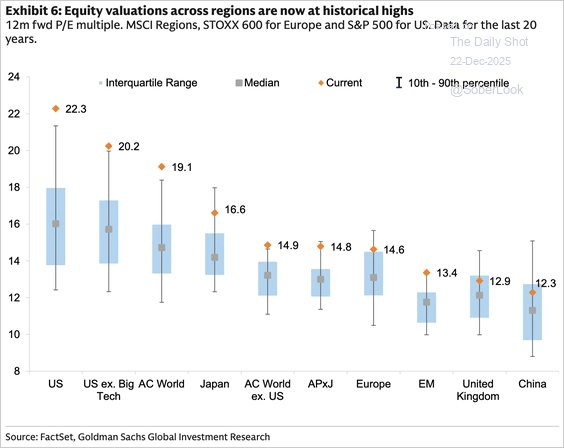
Stocks are still the most expensive in the United States, by far, but the rest of the world also became more expensive this year after an enormous rise in global stock prices almost everywhere.